Springboot MVC 파헤치기(12) ControllerAdvice 알아보기
ControllerAdvice 혹은 RestControllerAdvice가 하는 일은 Controller에서 발생한 예외를 받아 처리해주는 역할을 합니다. 저희는 이것을 어노테이션을 붙여주는 것만으로 사용할 수 있습니다. 간단한 예시를 보고, 어떻게 동작하는지 살펴보겠습니다.
1. ControllerAdvice 예시
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "gugus.pleco.domain") public class ControllerAdvice { @ExceptionHandler(UserDuplicatedException.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST) public ErrorDto duplicate1(UserDuplicatedException e){ return new ErrorDto(e.getMessage(),false); } @ExceptionHandler @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST) public ErrorDto duplicate2(UserDuplicatedException e){ return new ErrorDto(e.getMessage(),false); } }
1-1. @RescControllerAdvice를 지정할 범위 선택
@RestControllerAdvice에는 적용할 범위를 정할 수 있는 여러 가지 속성이 있습니다. 생략할 경우 전역에 해당합니다.
1. value, basePackaged: 해당 패키지와 하위 패키지에 적용

2. basePackageClasses: 해당 패키지 내에 클래스를 지정하여 적용

3. assignalbeTypes: 타입을 직접 지정하여 적용

4. annotations: 어노테이션이 붙은 것에 적용
1-2. @ExceptioHandler를 통해서 어떠한 예외를 잡는지 명시합니다. 이때 예외를 처리 하는 우선순위가 있습니다.
1. 자식 클래스
2. 부모 클래스
자식 클래스의 예외를 처리하는 @ExceptionHandler가 있다면, 동작합니다.
하지만 없다면 부모 클래스 예외를 처리하는 @ExceptionHandler가 동작합니다.
1-3. @ExceptionHandler 속성 생략
Handler로 들어오는 예외가 명시돼 있다면, @ExceptionHandler에 예외 클래스 속성을 생략할 수 있습니다.
2. ControllerAdvice 등록 과정
저희는 간편하게 어노테이션을 사용해서 ControllerAdvice를 등록할 수 있습니다. 과정을 살펴보겠습니다.
2-1. @ControllerAdvice와 @RestControllerAdvice는 Bean으로 등록됩니다.
@ControllerAdvice는 @Component를 가지고 있기 때문입니다.


2-2. ControllerAdviceBean에서 ControllerAdvice의 리스트를 반환하도록 합니다.
컨테이너 초기화 시점에 ControllerAdviceBean에서 Bean으로 등록된 ControllerAdvivce를 찾게 됩니다.
public static List<ControllerAdviceBean> findAnnotatedBeans(ApplicationContext context) { ListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context; if (context instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) { beanFactory = ((ConfigurableApplicationContext) context).getBeanFactory(); } List<ControllerAdviceBean> adviceBeans = new ArrayList<>(); for (String name : BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(beanFactory, Object.class)) { if (!ScopedProxyUtils.isScopedTarget(name)) { // ControllerAdivce를 찾는 과정 ControllerAdvice controllerAdvice = beanFactory.findAnnotationOnBean(name, ControllerAdvice.class); if (controllerAdvice != null) { adviceBeans.add(new ControllerAdviceBean(name, beanFactory, controllerAdvice)); } } } OrderComparator.sort(adviceBeans); return adviceBeans; }
findAnnotationOnBean은 DefaultListableBeanFactory의 메서드입니다.
ControllerAdviceBean에서 호출하는 함수는 findAnnotationsOnBean(String beanName, Class <A> annotationType)이고, 반환 값으로 내부에서 따로 호출하는 findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class <A> annotationType, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit)입니다.
@Override @Nullable public <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { return findAnnotationOnBean(beanName, annotationType, true); } @Override @Nullable public <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean( String beanName, Class<A> annotationType, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException { // 만약 ControllerAdvice 어노테이션이 붙은 Bean이라면 객체를 반환하고, 아닐 경우 null을 반환합니다. return findMergedAnnotationOnBean(beanName, annotationType, allowFactoryBeanInit) .synthesize(MergedAnnotation::isPresent).orElse(null); }
2-3. ControllerAdviceBean와 @ExceptionHandler로 붙여둔 예외를 맵핑
List로 반환된 ControllerAdviceBean들은 @ExceptionHandler로 붙여둔 예외를 맵핑하기 위해 ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver를 통해서 선언된 예외들과 ControllerAdivce를 맵핑합니다.
이로써 예외를 핸들할 수 있는 ControllerAdvice가 생깁니다.
public ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver(Class<?> handlerType) { for (Method method : MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(handlerType, EXCEPTION_HANDLER_METHODS)) { for (Class<? extends Throwable> exceptionType : detectExceptionMappings(method)) { // 예외를 맵핑 addExceptionMapping(exceptionType, method); } } } /* 예외를 맵핑해주는 메서드 파라미터 타입을 확인함으로써 맵핑합니다. 그래서 @ExceptionHandler 의 속성으로 예외를 주지 않아도 됩니다. */ private List<Class<? extends Throwable>> detectExceptionMappings(Method method) { List<Class<? extends Throwable>> result = new ArrayList<>(); detectAnnotationExceptionMappings(method, result); if (result.isEmpty()) { for (Class<?> paramType : method.getParameterTypes()) { if (Throwable.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) { result.add((Class<? extends Throwable>) paramType); } } } if (result.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException("No exception types mapped to " + method); } return result; }
3. ControllerAdvice 동작 과정
3-1. 요청의 시작과 끝인 DispatcherServlet에서 예외 핸들
요청 시작시에 dispatchException이 null로 시작하며, 예외가 없을 시 null로 있을 시 해당 예외가 들어갑니다. 예외가 발생했다면, processDispatcherResult로 null이 아닌 예외가 들어가게 됩니다.
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { /* 중략 */ try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; /* 중략 */ catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); /* 중략 */ }
예외가 null이 아니고, ModelAndViewDefinitionException이 아닌 경우 processHandlerException를 수행합니다. 예외 핸들을 위한 로직이 있습니다.
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } /* 중략 */ }
exMv =null로 시작해서 예외를 핸들 할 수 없다면, exMv가 null로 함수의 마지막에 다다르게 됩니다. throw ex이므로 예외를 터트리게 됩니다.
protected ModelAndView processHandlerException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { request.removeAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE); ModelAndView exMv = null; if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) { for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) { // 예외를 처리할 수 있는지 확인하며, 없다면 null을 반환하게 된다. exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (exMv != null) { break; } } } if (exMv != null) { /* 중략 */ } // 처리할 수 있는 예외 핸들러가 없으므로 결국에는 예외가 발생한다. throw ex; }
3-2. AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver에 존재하는 resolveException 실행
위에서 살펴본 resolveException의 경우 AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver의 메서드입니다. shouldApplyTo를 통해서 예외를 핸들 할 수 있는지, 확인하고 없다면 null을 반환합니다.
@Override @Nullable public ModelAndView resolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) { prepareResponse(ex, response); ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (result != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && (this.warnLogger == null || !this.warnLogger.isWarnEnabled())) { logger.debug(buildLogMessage(ex, request) + (result.isEmpty() ? "" : " to " + result)); } logException(ex, request); } return result; } else { return null; } } protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) { if (handler != null) { if (this.mappedHandlers != null && this.mappedHandlers.contains(handler)) { return true; } if (this.mappedHandlerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> handlerClass : this.mappedHandlerClasses) { if (handlerClass.isInstance(handler)) { return true; } } } } return !hasHandlerMappings(); }
위에서 에러를 핸들하기 위해서 실행하는 doResolveException는 AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver의 메서드입니다. doResolverHandlerMethodException의 구현체는 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver입니다.
@Override @Nullable protected final ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (handler instanceof HandlerMethod ? (HandlerMethod) handler : null); return doResolveHandlerMethodException(request, response, handlerMethod, ex); } @Nullable protected abstract ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception ex);
InvokeAndHandler -> InvokeForRequest -> doInvoke를 호출하는 형태로 진행됩니다.
@Override @Nullable protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) { ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception); if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) { return null; } /* 중략 */ try { /* 중략 */ // 예외를 처리할 수 있는 핸들러가 있다면, ServletInvocableHandlerMethod가 있다면 invokeAndHandler호출 exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments); } catch (Throwable invocationEx) { // Any other than the original exception (or a cause) is unintended here, // probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like). if (!exceptions.contains(invocationEx) && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Failure in @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx); } // Continue with default processing of the original exception... return null; } /* 중략 */ } }
doInvoke를 잠시 살펴보면 리플렉션 API를 이용해서 ExceptionHandler의 구현 메서드를 호출해서 에러를 처리합니다.
@Nullable protected Object doInvoke(Object... args) throws Exception { Method method = getBridgedMethod(); try { if (KotlinDetector.isSuspendingFunction(method)) { return CoroutinesUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction(method, getBean(), args); } return method.invoke(getBean(), args); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { assertTargetBean(method, getBean(), args); String text = (ex.getMessage() != null ? ex.getMessage() : "Illegal argument"); throw new IllegalStateException(formatInvokeError(text, args), ex); } /* 중략 */ }
4. ControllerAdvice VS ResponseEntityExceptionHandler
이전 Validation을 처리하면서 적용했던 @RestControllerAdvice가 존재하는 ResponseEntityExceptionHandler와 ControllerAdvice 중에서 어떤 것이 선택돼 에러를 처리하는지에 대해서 궁금증이 생겨서 테스트를 진행했습니다.
BeanValidation 적용 객체
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class UserDto { @Email(message = "email 형식으로 기입해주세요.") public String email; @Size(min = 8, max = 16, message = "password의 길이는 8~16자리로 해주세요.") public String password; @Range(min = 0, max = 100, message = "age는 0~100 사이로 입력해주세요.") public Long age; }
ResponseEntityExceptionHandler를 상속받아 Bean Validation을 처리하는 객체
@RestControllerAdvice(basePackages = "com.example.mvc") @RequiredArgsConstructor public class UserValidationHandler extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler { private final TypeMismatchConvertor typeMismatchConvertor; @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleMethodArgumentNotValid(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().stream() .forEach(a -> { String fieldName = ((FieldError)a).getField(); String message = a.getDefaultMessage(); map.put(fieldName,message); }); return new ResponseEntity<>(map, HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST); } @Override protected ResponseEntity<Object> handleHttpMessageNotReadable(HttpMessageNotReadableException ex, HttpHeaders headers, HttpStatus status, WebRequest request) { TypeMismatchConvertor.Result convert = typeMismatchConvertor.convert(ex.getMessage()); return new ResponseEntity<>(convert,HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST); } }
@RestControllerAdvice가 붙은 UserControllerAdvice 객체
@RestControllerAdvice public class UserControllerAdvice { @ExceptionHandler @ResponseStatus public String test(MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) { return "ok"; } @ExceptionHandler @ResponseStatus public String test2(HttpMessageNotReadableException ex) { return "ok"; } }
Controller는 이전 예제에서 봐주시길 바랍니다.
실험 예제 localhost:8080/validation/v6로 아래와 같은 요청을 보냈을 때 UserControllerAdvice가 동작한다면, "ok"를 UserValidatorHandler가 동작한다면 기존에 설정한 에러메시지가 나옵니다.

결과는 UserControllerAdvice가 동작됐습니다. 그 이유를 알아보자면 Bean 등록 순서와 상관이 있습니다. ComponentScan의 경우 @ComponentScan이 명시된 패키지부터 하위 패지키들을 순서대로 Bean으로 등록합니다. 이때 @SpringbootApplication이 있는 곳이 시작점이 됩니다.
현재 저의 패키지 구조입니다. controller가 handler보다 위에 있으므로 먼저 등록되므로 UserControllerAdvice가 동작했습니다.
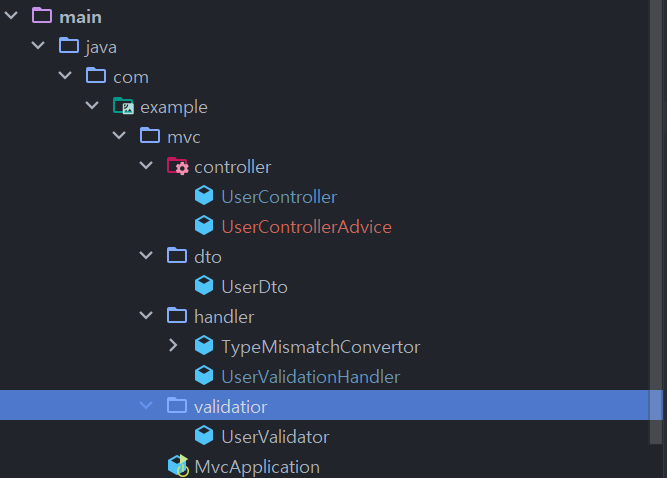
패키지 구조를 아래와 같이 바꿨을 때의 동작을 보겠습니다.
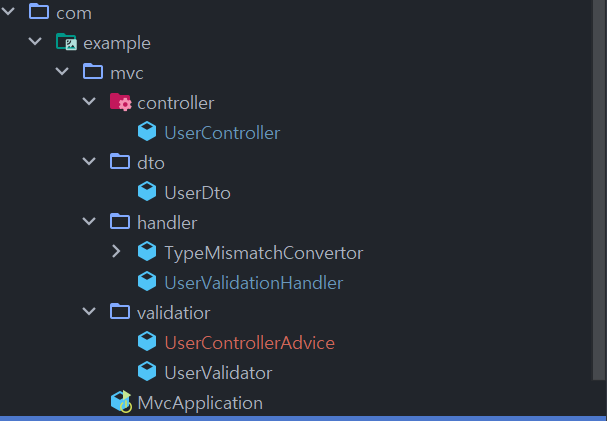
추측대로 UserValidationHandler가 예외를 처리했습니다.
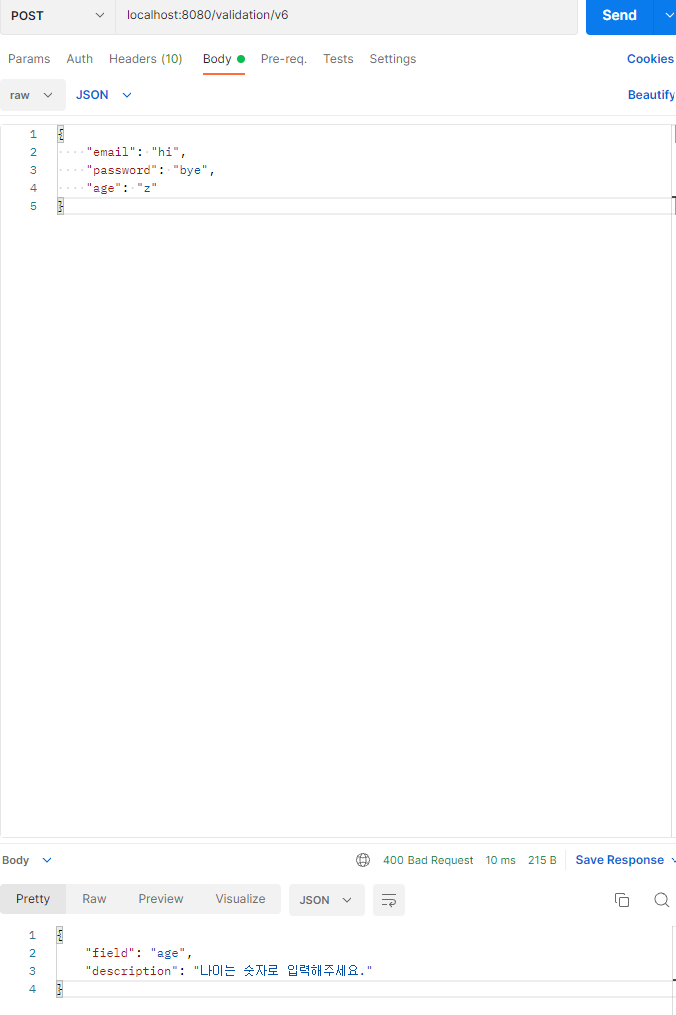
따라서 @Bean으로 등록할 위치에 따라서 결과가 달라집니다. 따라서 예외 처리 전략을 아래와 같이 정한다면, 효율적으로 다룰 수 있을 것이라고 생각합니다.
Bean Validation의 일관적인 예외처리 -> ResponseEntityExceptionHandler
비즈니스 로직을 실행하며 발생한 예외 처리 -> ControllerAdvice
'SpringBoot > spring mvc' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Springboot MVC 파헤치기(13) Collection Validation 적용 (0) | 2022.05.19 |
|---|---|
| Springboot MVC 파헤치기(11) Validation 동작과정 (0) | 2022.04.23 |
| Springboot MVC 파헤치기(10) Validation 유효성 검증 (0) | 2022.04.20 |
| Springboot MVC 파헤치기(9) ViewResolver, HttpMessageConverters (0) | 2022.03.16 |
| Springboot MVC 파헤치기(8) @ModelAttribute, @RequestParam, @PathVariable @ResponseBody @RequestBody 동작 과정 (0) | 2022.03.15 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(13) Collection Validation 적용
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(13) Collection Validation 적용
2022.05.19 -
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(11) Validation 동작과정
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(11) Validation 동작과정
2022.04.23 -
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(10) Validation 유효성 검증
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(10) Validation 유효성 검증
2022.04.20 -
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(9) ViewResolver, HttpMessageConverters
Springboot MVC 파헤치기(9) ViewResolver, HttpMessageConverters
2022.03.16
댓글을 사용할 수 없습니다.